Zhang et al. have introduced iDNAdrive, an innovative platform that enables users to encode their own data into DNA through the use of epigenetic modifications. This approach allows for a more accessible and personalized method of data storage, where individuals can actively participate in the encoding process.
- Utilizes DNA methylation to store information, allowing for multiple layers of data in a single DNA template.
- Enables controlled changes to encoded binary data through chemical reactions.
- Achieves synthesis-free writing of ~270,000 bits using a set of 700 DNA movable types and 5 templates.
- Employs an automated platform capable of writing 350 bits per reaction.
- Retrieves data encoded in complex epigenetic patterns using high throughput nanopore sequencing.
- Demonstrates potential for parallel, programmable, stable, and scalable DNA-based data storage.
DNA digital data storage has emerged as a cutting-edge approach to information preservation, combining the principles of molecular biology with advanced data encoding techniques. As reported by researchers from the University of Minnesota, this technology leverages DNA's incredible storage density and longevity to potentially revolutionize how we archive digital information.
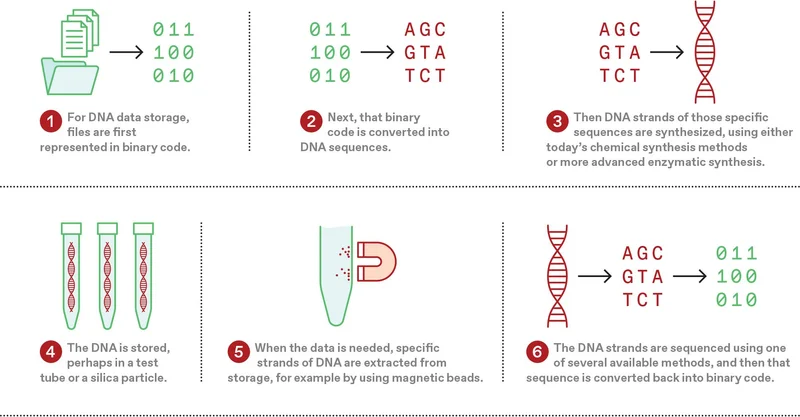
How DIY DNA Data Storage Works
Encoding Data: Data is converted into binary format (0s and 1s), which is then translated into DNA sequences using nucleotide bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine). This process can be done using various methods, including
- De novo synthesis: Traditionally, this involves synthesizing DNA from scratch, one nucleotide at a time.
- Epigenetic modifications: Recent advancements allow for encoding data directly onto pre-made DNA templates through chemical modifications like methylation, where methylated bases represent binary 1s and unmethylated bases represent 0s.
Storage: Once the data is encoded in the DNA, it can be stored in a stable environment. Properly encapsulated DNA can last for decades at room temperature and potentially much longer under controlled conditions.
Retrieval: To read the data, sequencing technologies such as nanopore sequencing are employed. This method allows for real-time reading of the DNA strands and their modifications, translating them back into binary files.

BENEFITS
- High Density: DNA can store vast amounts of information in an incredibly small volume. For instance, all of humanity's data could theoretically fit into a volume the size of a ping-pong ball.
- Durability: DNA is more durable than traditional storage media like hard drives and magnetic tapes, with the potential to last thousands of years if stored correctly.
- Energy Efficiency: Once encoded, DNA does not require energy to maintain its state, making it a passive storage solution.
Challenges
Current implementation challenges for DNA digital data storage include prohibitively high synthesis costs, estimated at $1 trillion per petabyte. Access times remain slow compared to conventional storage methods, and the encoding/decoding processes are complex. Temperature sensitivity necessitates controlled environments for data preservation. Additionally, the technology requires sophisticated laboratory equipment and expertise, making it unsuitable for DIY implementation at present. Researchers are actively working to address these limitations, with a focus on improving parallel writing mechanisms, error correction methods, and random-access capabilities to enhance the practicality of DNA-based storage systems.
"However, it is a revolutionary discovery, soon going to change the world".
Investment Ideas
Investors can align themselves with the evolving landscape of DNA data storage technology, particularly platforms that promise to transform how we think about digital information preservation.
Invest in DNA Storage Startups
Biomemory: This Paris-based startup has launched DNA cards that allow users to store data in a compact format. Their cards, priced at $1,000 for one kilobyte of data, highlight the potential for high-value, long-term storage solutions. As they aim to expand storage capacity and longevity guarantees, investing in Biomemory could yield returns as demand for sustainable data storage grows.
GenScript: This company claims to have the first commercially available DNA digital data storage platform. Their successful encoding and retrieval of mixed data types suggest a robust technology ready for market application. Investing in GenScript could be strategic as they seek partners to expand their technology's applicability.
Others such as Catalog Technologies, Helixworks Technologies, Evonetix may also work for you.
Funding R&D Initiatives
Investing in research initiatives or funds that support DNA technology development can yield long-term benefits as breakthroughs emerge from academic and corporate labs.
Genome Technology Program (NHGRI)
- Overview: This program supports research to innovate and develop new methods for rapid, low-cost nucleic acid sequencing and genotyping. It aims to achieve significant improvements in genomic technologies.
- Funding Opportunities: The NHGRI has issued Notices of Special Interest (NOSI) for advancing genomic technology development for research and clinical applications, encouraging applications that focus on novel laboratory tools.
- Website: More information can be found on the NHGRI website.
2. $1,000 Genome Program
- Overview: Launched by the NHGRI, this program focuses on reducing the cost of DNA sequencing to broaden its applications in biomedical research and healthcare.
- Funding Details: The program has funded various projects aimed at developing new DNA sequencing techniques, including nanopore technology.
- Website: Details about the program are available on the NHGRI's $1,000 Genome Program page.
3. Technology Development Seed Grants (Beckman Center, Stanford University)
- Overview: This program stimulates collaborations across disciplines to translate research discoveries into therapeutic applications. It supports high-risk, high-reward projects.
- Funding Amount: Grants provide up to $100,000 per year for two years to promising proposals.
- Website: More information can be found on the Beckman Center's website .
4. ICGEB Research Grants
- Overview: The International Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (ICGEB) offers funding for projects addressing significant scientific problems relevant to member countries.
- Funding Amount: Grants can provide up to €25,000 per year for a maximum of 36 months, supporting basic science and biotechnology research.
- Website: Further details are available on the ICGEB grants page .
5. Somatic Cell Genome Editing Program (NIH)
- Overview: This NIH program aims to advance genome editing technologies with an emphasis on developing new tools and approaches.
- Funding Amount: Recent awards totaled approximately $89 million across various projects aimed at enhancing genome editing capabilities.
- Website: More information can be found in the NIH announcements regarding the program.
Investing in these initiatives could provide exposure to groundbreaking advancements in DNA technology. By supporting programs that focus on innovative genomic solutions, investors may benefit up to millions, it is a similar case to elon musk revolutionary idea made billions.